Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) |
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Three types of foam currently used in panels are urethane, extruded polystyrene (XPS), and expanded polystyrene (EPS). Urethane cores are laminated to the skins with either an adhesive or by an injected in liquid form between separated skins. XPS and EPS cores must be laminated. In this writing, we will focus on XPS and EPS. |
| Advantages of XPS: - High R-value - Resistance to moisture - Impervious to rot, mildew, and corrosion - Light and easy to work with - Closed cell - Smooth cut-cell surface |
| Advantages of EPS: - Light and easy to work with - When cutting with a hot wire, there is no dust - Accepts various glues and mastics - Bonds well to the skins |
| A measurement of panels is the R-value. The R-value is a measure of resistance to thermal conduction. Since heat conducts through walls and roofs all over, not just where the insulation is, building heat loss is calculated over the "whole surface". The problem comes from the fact that most insulations are labeled and sold based on their in-cavity R-value. Additionally, most residential energy codes are written assuming stick framing will be used and only specify the infill R-value. The following table allows easy conversion from center of cavity R-values to whole surface R-values and back again. |
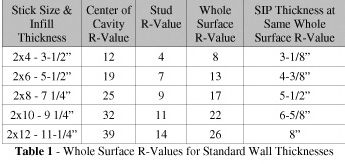 |
| Looking at this another way, you can choose a SIP or Whole Surface R-Value and calculate the thickness of stick and infill wall. |
 |
| Different types of commonly
used panels are: - Drywall clad - Structural panel - Nailbase panel - Curtainwall panel |
| Drywall clad is drywall layered
over OSB layered over either XPS or EPS layered over OSB. Structural panel is OSB, XPS or EPS, OSB. Nailbase panel is XPS or EPS layered over OSB. Curtainwall panel is drywall, XPS or EPS, OSB. |
| Both drywall clad and structural panels are load bearing panels. Nailbase and curtainwall panels are not. Nailbase panels are an alternative to “wrap and strap” insulation and sheathing systems. Curtainwall panels can be used for walls and short span roofs. |
©
Copyright 1999-2010. South County Post & Beam, Inc. |
